Peacksoft PSA Workflow.
Peacksoft Professional Service Automation
Professional Service Automation (PSA) in the project industry refers to a comprehensive set of tools and processes that streamline the management of services in project-based businesses. It covers the full project lifecycle, from planning and resource management to execution, billing, and analytics. By integrating all aspects of project management, PSA improves efficiency, transparency, and profitability.
Key Features of PSA in Project Industry:
1. Project Management:
Project Planning: PSA systems help in defining project scope, creating work breakdown structures (WBS), setting milestones, and tracking deliverables.
Task & Milestone Templates: Users can create predefined task templates for recurring projects to streamline the process.
Task Assignment: Allocate tasks and responsibilities to team members based on skills, availability, and workload.
Gantt Charts: Visualize project timelines and track the status of various tasks, milestones, and dependencies. Risk Management:Identify potential risks, define mitigation strategies, and monitor risk levels throughout the project.
2. Resource Management:
Resource Allocation: Assign people, machines, materials, and expenses to different tasks within the project. Track their availability and utilization.
Resource Optimization: Maximize the efficient use of available resources by preventing under- or over-allocation.
Capacity Planning: Ensure that resources such as employees and equipment are adequately available for current and future projects.
Billing & Cost Rates: Set billing rates and cost rates for each resource, contributing to cost tracking and overall project budgeting.
3. Time & Expense Management:
Timesheets: Employees and contractors can log the time spent on specific tasks and activities, which can be used for billing and performance tracking.
Expense Tracking: Record project-related expenses such as travel, materials, and services to ensure accurate financial management.
Mobile Accessibility: Enable real-time time and expense logging via mobile apps, improving accuracy and timeliness.
4. Financial Management:
Project Budgeting: Set up initial budgets for projects, including expected revenues and expenses.
Revenue Forecasting: PSA systems can estimate revenue generation based on milestones achieved and the project's progress.
Invoicing & Billing: Automate billing based on project progress (e.g., time & materials, fixed price, milestone-based billing). Integration with accounting systems helps in generating invoices with accurate data.
Profitability Tracking: Monitor the financial performance of each project by comparing actual costs against projected budgets.
5. Collaboration Tools:
Document Management: Store and manage project documents, contracts, designs, and communications in a central location for easy access.
Team Collaboration: Facilitate communication and collaboration through chat, project forums, or integrated tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams.
Client Collaboration: Provide clients with access to specific parts of the project, enabling them to monitor progress, approve milestones, and provide feedback.
6. Automation of Project Execution:
Task Automation: Automate repetitive tasks such as creating recurring deliverables or sending status reports.
Workflow Automation: Define custom workflows for approvals, task assignments, and milestone sign-offs.
Reporting Automation: Automatically generate and send periodic reports to stakeholders based on project status, resource usage, and financial data.
7. Analytics & Reporting:
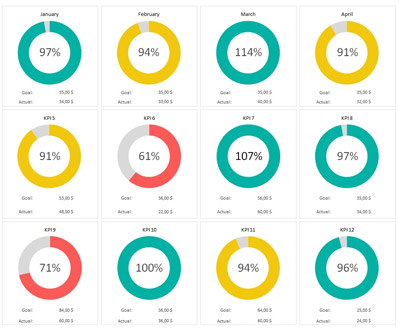
KPI Dashboards: Display key performance indicators such as project progress, resource utilization, financial health, and timeline adherence in real-time.
Real-Time Monitoring: Gain insights into the project's status and performance metrics to ensure that milestones are on track.
Custom Reports: Create customizable reports on resource usage, project profitability, budget variances, and more.
Predictive Analytics: Use historical data to predict potential project risks, delays, and resource shortages.
8. Client Relationship Management (CRM) Integration:
Client Tracking: Manage client relationships, track interactions, and monitor the sales pipeline within the PSA system.
Proposals & Contracts: Generate proposals based on project requirements, including automatic cost and time estimates. Convert approved proposals into project plans.
Client Billing: Send automated invoices and keep track of client payments, linking to project progress to ensure timely billing.
Benefits of PSA in the Project Industry:
Increased Efficiency: Automates routine tasks, reduces manual data entry, and streamlines the project lifecycle. Improved Project Visibility: Provides real-time visibility into all aspects of project performance, enabling proactive decision-making. Enhanced Resource Utilization: Ensures resources are used optimally, reducing downtime and maximizing billable hours. Financial Accuracy: Tracks project costs, billable hours, and expenses with accuracy, reducing the risk of budget overruns and delayed billing. Collaboration & Communication: Improves team collaboration and communication both internally and with clients. Scalability: PSA systems can be scaled to handle multiple projects simultaneously, adapting to project growth and complexity. Improved Client Satisfaction: Timely delivery, transparent communication, and effective management result in higher client satisfaction levels.
By incorporating PSA solutions, companies in the project industry can enhance project management, resource planning, and financial control, leading to more successful project outcomes.
Professional Service Lead/Enquiry
Professional Services Automation (PSA) software significantly enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of project delivery in various ways:
Key Features of PSA
1. Project Management:
Enables the creation and management of project plans, timelines, and milestones. Facilitates collaboration among team members to ensure project goals are met on time.
2. Resource Management:
Allows for allocation and optimization of resources based on project needs. Tracks resource availability, skill sets, and utilization rates.
3. Contract Management:
Streamlines the creation, storage, and management of contracts with clients. Ensures compliance with contractual obligations throughout the project lifecycle.
4. Invoicing and Billing:
Automates the invoicing process based on project milestones and time tracking. Facilitates accurate billing with customizable invoicing templates.
5. Proposal Management:
Assists in creating detailed project proposals and cost estimates. Provides templates and tools for tracking proposal submissions and follow-ups.
6. Team Collaboration:
Integrates communication tools to enhance collaboration among team members. Supports file sharing, real-time updates, and feedback mechanisms.
7. Project Tracking:
Offers dashboards and reports for monitoring project progress and performance metrics. Enables identification of bottlenecks and timely decision-making.
8. Time & Expense Tracking:
Simplifies the process of logging work hours and expenses incurred during the project. Integrates with billing systems to ensure accurate invoicing based on tracked time.
Document Management:
Centralizes the storage of project-related documents, contracts, and communications. Ensures version control and easy access to critical information for all team members.
Benefits of PSA Software Increased Efficiency: Streamlines various project management tasks, reducing manual efforts and errors. Enhanced Visibility: Provides real-time insights into project status, resource allocation, and financial performance. Improved Client Relationships: Ensures timely communication and transparency with clients throughout the project lifecycle. Data-Driven Decisions: Centralized data allows for informed decision-making and strategic planning.
PSA software serves as a comprehensive solution for service organizations, facilitating better management of client engagements and enhancing overall project delivery.





Resource Management
The Resource Management feature in PSA software plays a crucial role in efficiently managing various types of resources throughout project execution. Here’s a detailed overview:
Resource Types
Labor: Includes all human resources allocated to a project. Their usage can be tracked in terms of hours worked, and they typically have associated billing rates per hour or day.
Material: Encompasses physical items or raw materials needed for project execution. Costs can vary based on quantity used and specific material types.
Expense: Covers additional costs incurred during the project that are not classified as labor or materials. This may include travel expenses, subcontractor fees, or other miscellaneous costs.
Item: Refers to specific products or goods that can be tracked and managed within the project. Items might have unique identifiers and can be linked to inventory management systems.
Key Features
1. Usage Tracking: Enables project managers to monitor how much of each resource type is being utilized throughout the project lifecycle.
2. Cost Management: Provides visibility into the costs associated with each resource type, helping in budget management and financial forecasting.
3. Billing Rates: Allows users to define billing rates for each resource based on the unit of measure (hour, day, month). This ensures accurate invoicing based on resource utilization.
4. Resource Allocation: Facilitates the assignment of resources to specific tasks or projects, ensuring optimal use of available resources.
Reporting: Generates reports on resource usage, costs, and billing, providing insights into project profitability and efficiency.
By effectively managing resources, PSA software helps organizations improve project delivery, optimize costs, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Contract
Project Contract is the terms and conditions agreed between parties and companies in terms of billing, delivery and other aspects




Project Invoicing
Project Invoicing in a PSA (Professional Services Automation) system is a structured process that converts resource usage, based on the project contract, into detailed invoices. It ensures that clients are billed accurately for the time, materials, and services used throughout the project lifecycle.
Contract-Based Invoicing:
Invoices are generated based on the terms defined in the project contract, which outlines the billing model—whether it's time and materials, fixed price, or milestone-based billing.
Billing Entries from Task Resources:
Each task within a project has associated resources (labor, materials, expenses, items).
For labor, billing entries are created based on the time spent (hours, days, or months).
Material, expense, and item costs are tracked and added based on usage.
The billing entries typically reflect the agreed-upon rates for each resource, which are multiplied by the actual usage (e.g., number of hours or days).
Rates and Resource Utilization:
Labor rates: Based on the hourly/daily/monthly billing rate for a resource. Material costs: Calculated as per the usage rate defined in the contract. Expense costs: For additional costs such as travel or equipment, these are billed based on the actuals incurred. Item costs: Direct cost of goods or products used in the project.
Time Tracking and Resource Costing:
In PSA, time tracking is essential for resources, especially labor, where users log hours/days worked on specific tasks. These logged hours/days are multiplied by the resource’s billing rate to calculate the billable amount.
Progressive Billing:
For long-term projects, invoicing may happen progressively, based on milestones or periodic billing cycles. This ensures that clients are billed at regular intervals (e.g., monthly), reflecting the actual progress of the project.
Invoice Generation:
The PSA system generates invoices by pulling data from task resources, including: Labor costs (hours/days worked multiplied by rate). Material costs (quantity used multiplied by price). Expense costs (such as travel or incidental charges). Item costs (goods used or delivered to the client).
The system can format these details into an invoice template that includes itemized details or summary-level billing, depending on the client’s requirements.
Invoice Adjustments:
In some cases, adjustments may need to be made, such as discounts, penalties, or additional charges like overtime or rush fees. The PSA system allows users to modify the billing entries to accommodate these changes before finalizing the invoice.
Tax and Compliance:
Depending on the region and contract, tax (e.g., GST, VAT) may need to be applied to the invoice. The system handles compliance with relevant tax regulations and automatically calculates taxes based on jurisdiction.
Invoice Review and Approval:
Once the invoice is generated, it may go through an approval process where managers or finance teams review it for accuracy before sending it to the client.
Delivery and Tracking:
After approval, the invoice can be sent to the client, either through the PSA system’s email integration or by exporting it to an external accounting system. The PSA system can track the invoice’s status (e.g., sent, pending payment, paid) to ensure timely follow-up on receivables.


Project Tracking
Project management is the process of leading a project from inception to closure, using techniques and tools to plan, organize, and control the work of a project team to achieve specific goals and objectives. It involves defining project scope, setting goals and objectives, creating a project plan, allocating resources, managing and monitoring progress, controlling changes, and closing the project. Project management requires effective communication, collaboration, and leadership skills to ensure that the project stays on track, meets its goals, and delivers the desired results within budget and on time. Project management techniques such as Agile, Scrum, Waterfall, and Lean are used to plan, execute, and close projects in various industries, including construction, software development, and product design.
Estimate & Proposal
In Peacksoft ERP, users can prepare a proposal and cost estimate by leveraging the project breakdown structure (PBS) to provide a comprehensive plan that includes tasks, resources, and timelines. This feature helps streamline the proposal process by allowing users to break down projects into smaller components, each with detailed cost estimates and tentative delivery schedules.
Project Breakdown Structure (PBS) Setup:
Define the tasks and milestones for the project.
Assign resources such as materials, personnel, and equipment to each task.
Specify duration and dependencies between tasks.
Cost Estimation:
Allocate Costs: Assign costs to each task or resource, including labor, materials, and overheads. Calculate the total project cost by summing individual task costs.
Billing Rates: Use the system’s billing rate structure to estimate the financial value of each resource or task.
Delivery Schedule:
Based on the task durations and resource availability, the system generates a tentative delivery schedule.
Adjust timelines by reviewing resource allocation and dependencies.
Include projected completion dates for specific milestones or phases.
Proposal Creation:
Use the cost estimate and delivery schedule to generate a professional project proposal. The proposal includes project scope, cost breakdown, and timeline. Customize the proposal format to align with client requirements.
Client Review and Approval:
Share the proposal with the client for review. Any changes made during negotiations can be updated directly in the system, with automated adjustments to costs and schedules.
This proposal and cost estimation feature helps users provide a clear project plan with detailed cost analysis and timeframes, improving client communication and ensuring projects are well-defined from the start.

Get Started with Peacksoft ERP Today
Intuitive solutions on cloud with integrated features like Accounting, Purchase, Sales, Production, CRM, Payroll, Inventory & Filing of all compliances. . Call us at +91-86608 58802 (M: 9845167247) to schedule a consultation.

 Manage sales through quotation by updating information and proceed to Sales order, Sales delivery , Sales invoice by click of few button.
Manage sales through quotation by updating information and proceed to Sales order, Sales delivery , Sales invoice by click of few button.
 Manage Purchases through order by updating information and proceed to GRN, Purchase Invoice by click of few buttons.
Manage Purchases through order by updating information and proceed to GRN, Purchase Invoice by click of few buttons.
 Comprehensive Inventory management features for small and mid size companies.
Comprehensive Inventory management features for small and mid size companies.
 Manufacturing
Manufacturing