
It offers complete solution of production enquiry, BOM design, production planning and control. Finished good BOM (Bill of Material), estimation of production process and routing, tracking production job in the work center are different stages supported by the ERP. It helps the company to track material cost, labour cost and overall production cost.

Production ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a specialized software solution designed to optimize and streamline manufacturing processes within an organization. By integrating various functions such as production planning, inventory management, quality control, and resource allocation, Production ERP provides a comprehensive view of the entire manufacturing operation.
The core objective of Production ERP is to enhance efficiency and productivity while reducing costs. It facilitates real-time tracking of materials and products, enabling manufacturers to respond quickly to changes in demand and supply chain dynamics. With features such as Bill of Materials (BOM) management, production scheduling, and job tracking, organizations can improve their planning accuracy and resource utilization.
Moreover, Production ERP fosters collaboration among departments, ensuring that everyone—from sales and purchasing to production and finance—is aligned with the organization's goals. By providing actionable insights through data analytics and reporting, Production ERP empowers decision-makers to make informed choices that drive growth and profitability.
In today's fast-paced and competitive manufacturing landscape, adopting a robust Production ERP system is essential for organizations seeking to enhance their operational efficiency and maintain a competitive edge.
- Provides more advanced functionality for manufacturing specific needs and workflow.
- Gives a 360-degree view of entire manufacturing process and workflow from the shop floor to final delivery warehouse.
- Allows for full-visibility and control over your manufacturing business to be more profitable.
- Use QC checkpoints to ensure final products meet customer specifications.
Work order
Work Order
In Peacksoft ERP, creating a Work Order from a confirmed Sales Order streamlines the production process. Here’s how it works:
Creating a Work Order from a Confirmed Sales Order
1. Select the Confirmed Sales Order:
a. Navigate to the Sales Order module and locate the confirmed Sales Order you wish to convert into a Work Order.
2. Initiate Work Order Creation:
a. Click on the option to create a new Work Order linked to the selected Sales Order.
3. Specify Required Details:
a. Quantity: Enter the specific quantity of the final goods required for production.
b. Release Date: Set the desired release date for the final goods, ensuring it aligns with customer expectations and production capacity.
4. Review and Confirm:
a. Review the details to ensure accuracy. The system may auto-populate relevant information such as product specifications and routing based on the linked Sales Order.
b. Confirm the Work Order to initiate the production process.
5. Manage Production Tasks:
a. Once the Work Order is created, it can be tracked through various stages of production. Users can assign tasks, monitor progress, and manage resources as necessary.
6. Link to Inventory:
a. The Work Order is connected to inventory management, ensuring that raw materials are allocated and tracked against the production requirements.
By integrating the Sales Order and Work Order processes, Peacksoft ERP enhances operational efficiency, enabling quick and accurate fulfillment of customer demands. This seamless transition helps maintain production schedules and improves overall service delivery.
Work Order Issue
In Peacksoft ERP, issuing raw materials for a given Work Order involves tracking material movement from inventory to the production floor. Here's how the process works:
Issuing Raw Materials for a Work Order
1. Select the Work Order:
a. Navigate to the Work Order module and choose the specific work order for which raw materials are needed.
2. Initiate Material Issue:
a. Click on the option to issue raw materials associated with the selected work order.
3. Specify Required Details:
a. Material Location: Select the location (warehouse, rack, bin) from where the raw materials will be sourced.
b. List of Raw Materials: The system will auto-populate the raw materials based on the Bill of Materials (BOM) linked to the work order. You can adjust quantities if necessary.
c. Date of Requirement: Input the date by which the raw materials are required for production.
4. Allocate Raw Materials:
a. Confirm the allocation of raw materials from stock to the work order. This ensures the required materials are reserved for the production process.
5. Transfer to Production Floor:
a. The system will record the movement of raw materials from inventory to the production area. A material issue request or stock transfer slip may be generated to track this movement.
6. Monitor Stock Levels:
a. The system will update inventory levels, reflecting the reduction in stock for the issued materials. It will also track real-time availability across different warehouse locations.
7. Approval Process (if applicable):
a. If required, send the material issue request for approval by authorized personnel before proceeding with the physical transfer.
8. Track Material Flow:
a. Once materials are issued, the system will track their usage against the work order. This ensures accurate monitoring of material consumption and production costs.
By efficiently issuing raw materials, Peacksoft ERP ensures that production schedules are met while maintaining accurate inventory tracking, helping avoid production delays and material shortages.
RM Planning
This process enables companies to effectively plan their raw material (RM) needs based on current open Sales Orders or Work Orders. Here’s how it works:
1. Demand Planning:
a. Sales Order and Work Order Integration: The system analyzes all open Sales Orders and Work Orders to determine the quantities of raw materials required for production.
b. Forecasting Needs: By evaluating current orders, companies can accurately forecast their raw material needs, ensuring they have the right quantities on hand.
2. Purchase Requisition Creation:
a. Automated Requisitions: Based on the calculated raw material requirements, users can create purchase requisitions for the needed materials.
b. Streamlined Procurement: This automated process facilitates the procurement workflow, enabling timely ordering of raw materials to avoid production delays.
3. Inventory Management:
a. Stock Levels Monitoring: The system helps maintain optimal inventory levels by linking production requirements with current stock, minimizing overstock or stockouts.
b. Enhanced Planning: Companies can align their procurement activities with production schedules, ensuring that raw materials arrive just in time for production needs.
4. Efficiency and Cost Savings:
a. Reduced Lead Times: By planning ahead, companies can reduce lead times for raw material procurement, enhancing overall production efficiency.
b. Cost Control: Efficient raw material planning helps in controlling costs associated with emergency orders or excess inventory.
This proactive approach to raw material management ensures that companies can meet production demands efficiently while optimizing their procurement processes.
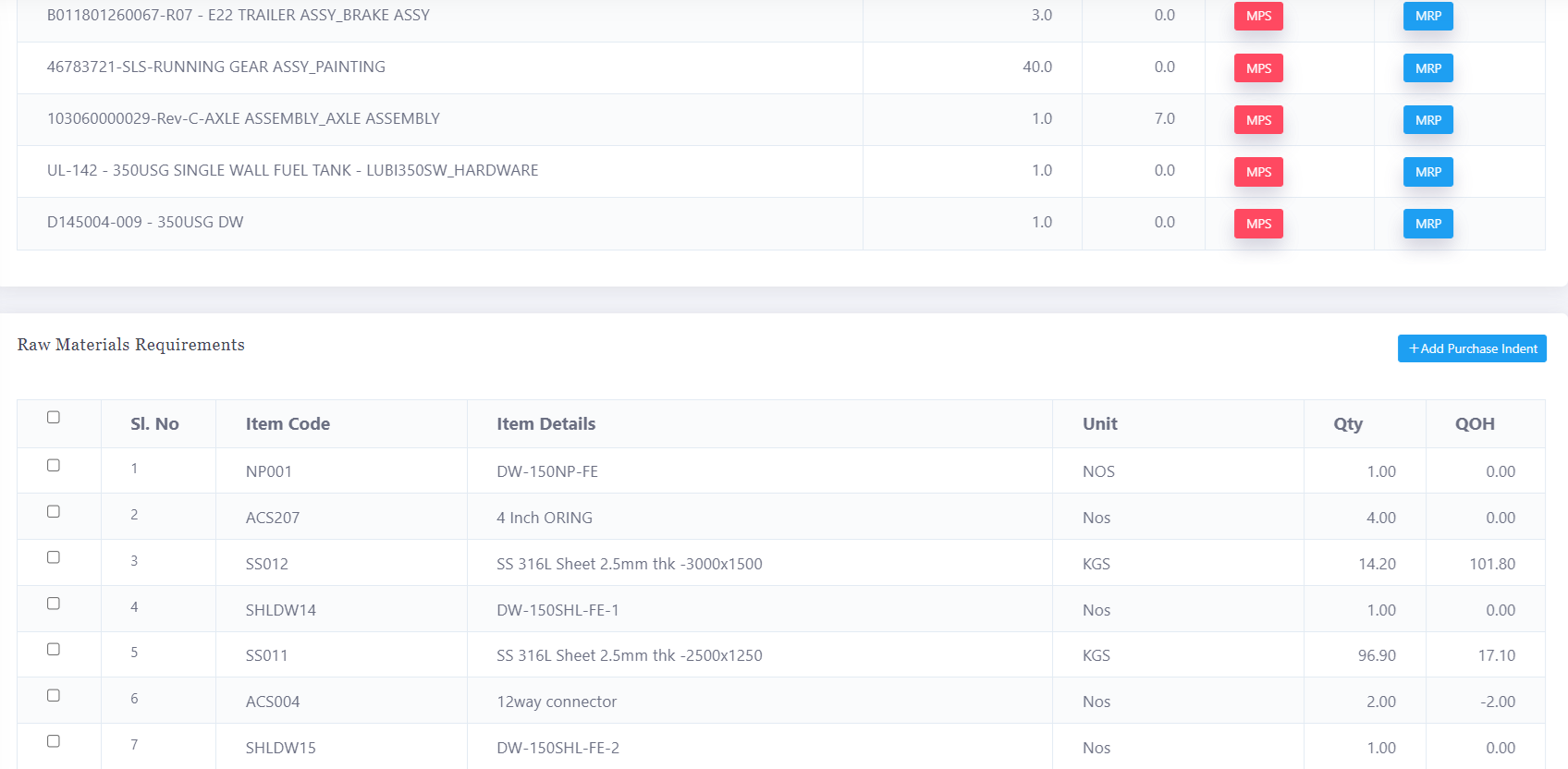
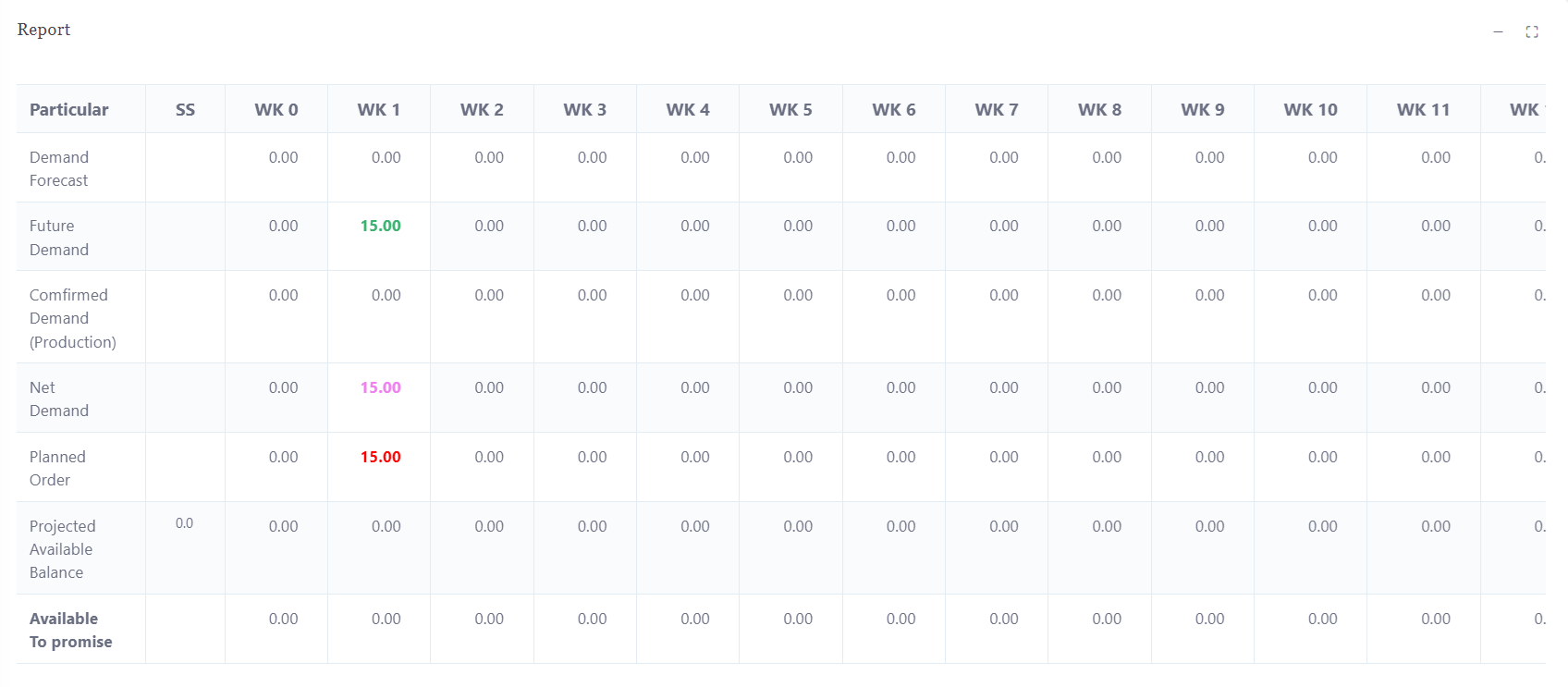

Master Production Schedule (MPS)
Master Production Scheduling (MPS) is a key planning tool that determines the what, when, and how much of production. It plays a vital role in synchronizing sales and manufacturing by ensuring that production meets customer demand efficiently. Here's how MPS functions and its significance:
Key Functions of Master Production Scheduling (MPS):
1. Product Planning:
a. MPS identifies which products need to be manufactured, specifies the production schedule, and determines the quantities required.
2. Linking Sales and Production:
a. MPS acts as a contract between the sales and manufacturing departments, ensuring that sales commitments align with production capacity.
b. It allows sales teams to make reliable promises to customers based on realistic production schedules.
3. Raw Material Procurement:
a. The MPS works with the Bill of Materials (BOM) for finished goods, identifying the required raw materials for each product.
b. These raw material needs are integrated with current inventory data, enabling an accurate Material Requirement Plan (MRP) for procurement.
4. Forecast-Based Planning:
a. MPS uses demand forecasts and current supply/demand data to develop accurate and timely production plans, which helps companies meet customer demand without overproduction.
5. Dynamic Scheduling:
a. The MPS is a dynamic tool that adapts to changing market conditions, customer demand, and capacity constraints. It can be updated as new data becomes available, allowing for flexibility in production planning.
6. Optimized Production Flow:
a. By ensuring production matches demand, MPS minimizes procurement costs by avoiding excess inventory and reducing lead times.
b. It also prevents production bottlenecks by balancing the demand with available resources.
Benefits of Master Production Scheduling:
a. Alignment of Sales and Production: Ensures that sales commitments are met with realistic production timelines.
b. Inventory Control: Prevents overstocking by linking production requirements to raw material availability through BOM and inventory integration.
c. Cost Efficiency: Reduces unnecessary procurement and storage costs by producing only what is needed, when it’s needed.
d. Adaptability: Allows quick adjustments to changes in demand, ensuring that production can respond to customer needs without delay.
e. Better Decision-Making: Provides a clear view of production schedules, enabling managers to make informed decisions on production priorities.
By leveraging MPS, manufacturers can ensure a smooth and efficient production process, improve customer satisfaction, and reduce operational costs, all while maintaining the flexibility to adjust to changing demands.
Material Requirement Planning (MRP)
Master Requirements Planning (MRP) is a critical system that helps manufacturers manage production and inventory efficiently by aligning supply with demand. Here's an overview of how MRP functions and its core benefits:
How MRP Works:
1. Data Collection from Sales Orders and Demand Forecasts:
a. MRP collects data from sales orders or demand forecasts to anticipate the needs for production.
b. The system ensures that the production aligns with actual or predicted customer demands.
2. Input from Master Production Schedule (MPS):
a. MRP receives instructions from the Master Production Schedule (MPS), which outlines the quantities of finished goods required based on sales orders or demand forecasts.
b. The MRP uses this data to determine the specific raw materials needed, derived from the Bill of Materials (BOM).
3. Bill of Materials (BOM) and Material Requirements:
a. By analyzing the BOM, the MRP identifies the raw materials necessary to produce the finished goods specified by the MPS.
b. It helps the system display exactly what materials need to be purchased or produced.
4. Supply and Demand Management:
a. MRP ensures that all supply and demand are aligned, bringing both onto the same page.
b. It generates purchase orders for raw materials or production orders for manufacturing, ensuring a smooth production process.
5. Demand Forecasting:
a. MRP can generate forecasts for finished goods based on customer orders, helping manufacturers anticipate future demand.
b. This is essential for planning purposes, especially in industries with fluctuating demand.
6. Just-In-Time Inventory Optimization:
a. One of the key goals of MRP is to enable just-in-time (JIT) inventory, ensuring that raw materials arrive exactly when needed for production.
b. This minimizes the need for excessive inventory storage and reduces waste, leading to cost savings and improved efficiency.
Benefits of MRP:
a. Accurate Material Planning: Ensures the correct materials are available for production at the right time, reducing delays and stockouts.
b. Demand Alignment: Helps manufacturers produce based on real-time demand forecasts and sales orders, preventing overproduction or shortages.
c. Improved Efficiency: Optimizes production and purchasing activities, ensuring smooth operations and reduced lead times.
d. Cost Savings: Minimizes inventory holding costs through just-in-time practices and reduces wastage.
e. Enhanced Forecasting: Provides valuable insights into future demand trends, allowing businesses to plan better and allocate resources more effectively.
Overall, MRP is an essential tool for aligning production, inventory, and purchasing with customer demand, helping companies improve productivity, lower costs, and respond flexibly to market changes.

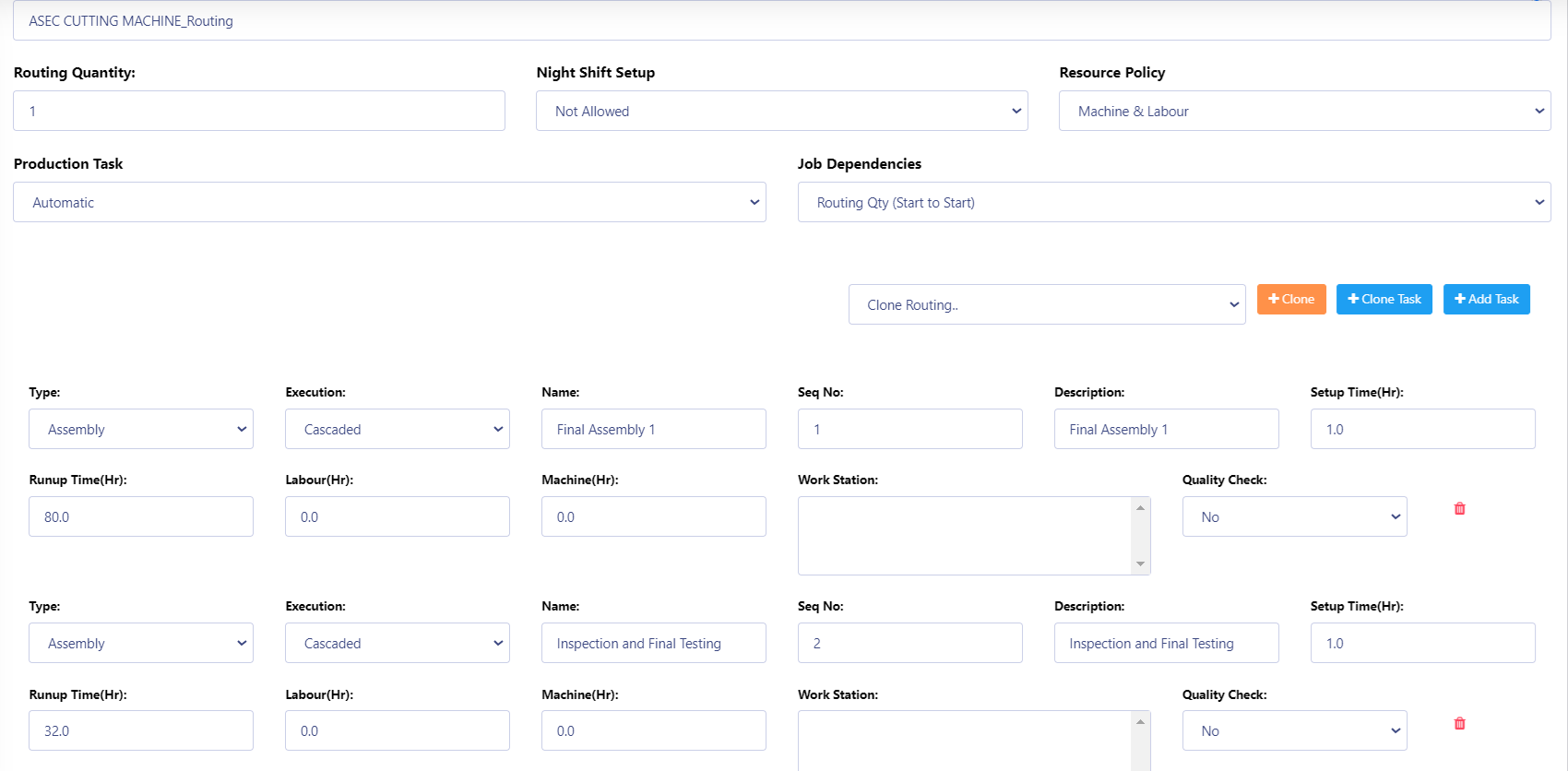
BOM & Routing
BOM & Routing in Peacksoft ERP is a crucial feature that helps users efficiently manage and plan the production of finished and semi-finished goods through structured Bill of Materials (BOM) and routing processes. Here’s how it works and its core benefits:
Key Features of BOM & Routing:
1. Multi-Level BOM Design:
a. Users can design a multi-level BOM for semi-finished and finished goods, mapping out the required quantities and raw material inputs at each production stage.
b. This structure enables better management of complex manufacturing processes that involve multiple stages of production or intermediate products.
2. Project-Based BOMs:
a. The system supports project-based BOMs, allowing users to link the BOMs to specific projects for more efficient management and tracking.
b. This feature is particularly beneficial in industries like manufacturing, construction, and engineering, where different projects may require varying levels of components.
3. Importing BOMs:
a. BOMs can be imported through Excel files, making it easier for users to integrate external BOM data into the system without manual entry, saving time and reducing errors.
4. Semi-Finished Goods BOM Creation:
a. Users can create BOMs not just for finished goods but also for semi-finished goods, where the input is raw materials that undergo certain processes.
b. This flexibility allows for the creation of multiple stages of production, with each stage having its unique BOM.
5. Routing:
a. Routing involves defining the production processes and sequences for manufacturing goods. It maps out the path that the product takes during production, including operations, work centers, and the time required for each stage.
b. Routing helps ensure smooth production workflows and efficient allocation of resources, such as machinery and labor, based on the defined process stages.
Benefits of BOM & Routing:
a. Streamlined Production Planning: With a well-structured BOM and routing system, users can plan the entire production process from raw materials to finished goods with precision.
b. Multi-Level BOM Flexibility: The ability to handle multi-level BOMs allows manufacturers to manage both simple and complex production workflows efficiently.
c. Project-Specific Management: Linking BOMs to specific projects provides better oversight and control over resources and timelines, making it easier to track costs and material usage.
d. Time and Error Reduction: Importing BOMs via Excel reduces manual data entry errors and speeds up the setup process, enabling faster execution of production plans.
e. Enhanced Efficiency: Routing ensures that each step of the production process is clearly defined, leading to better coordination between departments, optimal use of resources, and reduced production delays.
This module helps streamline manufacturing processes, ensures better inventory management, and ultimately boosts productivity across all stages of production.
Production
The production process in Peacksoft ERP begins with capturing customer requirements and proceeds through multiple stages of planning, scheduling, and execution to deliver finished goods. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
1. Enquiry and Production Design
a. Customer Enquiry: The system captures customer requirements, including the quantity of finished goods and the due date, through an enquiry.
b. Design Record: Based on the enquiry, a production design is created. This includes the speculation of resources, machines, labor, and materials required to fulfill the production as per the design document.
2. Bill of Materials (BOM) Creation
a. Once the design is finalized, a BOM for Finished Goods (FG) is created. This includes all the necessary raw materials, components, and any semi-finished goods required to produce the final product.
3. Work Order Generation
a. A Work Order is then raised in the system, sent to the production department. It specifies the production quantity, due dates, and any specific requirements based on the customer’s enquiry and design document.
4. Material Requisition & Production Planning
a. Material Requisition: The system checks the raw materials required for production, and if materials are not available, a purchase requisition is created.
b. Production Planning: This stage involves scheduling machines, labor, and raw materials (RM) to ensure timely production. The Production Schedule is finalized based on availability and capacity, with considerations for machine and labor utilization.
5. Job Creation and Task Management
a. When production starts, specific jobs are created for each phase of the production process. This breaks down the work into manageable tasks for tracking and completion.
b. Each job can be linked to specific machines, labor, or processes, with user-defined task milestones for monitoring progress.
6. Tracking and Updates
a. Throughout the production cycle, the system allows users to follow and manage job tasks. This includes tracking the progress of each job, updating the status, and ensuring timely completion of tasks.
b. The system also supports real-time updates on material usage, machine performance, and labor efficiency to keep the production process on track.
7. Completion and Handover
a. Once all job tasks are completed, the finished goods are produced, inspected (if required), and ready for delivery or storage.
b. The work order is closed, and the system records all relevant production details, ensuring a complete record of resource utilization, costs, and output for future analysis.
Key Benefits:
a. Streamlined Production: Ensures smooth coordination from customer enquiry to finished goods production, reducing delays and bottlenecks.
b. Efficient Resource Utilization: Accurate planning and scheduling help optimize the use of materials, machines, and labor.
c. Real-Time Tracking: The ability to track jobs and tasks ensures that production managers can monitor progress and intervene when necessary.
d. Improved Decision-Making: Detailed records of material usage, machine efficiency, and labor productivity allow for better decision-making and resource allocation in future projects.
This process ensures that Peacksoft ERP provides comprehensive control over production, from planning to execution, allowing businesses to meet customer demands efficiently.
Read more on Production ERP Details
Production Planning & Control in Peacksoft ERP is an automated and intelligent system designed to streamline manufacturing operations by considering multiple variables like production jobs, machines, labor, and capacity. Here's how it works:
1. Automated Production Planning
a. Integrated Process: The system automatically manages production jobs by analyzing real-time data on machine availability, labor capacity, and job priorities, minimizing manual intervention.
b. Dynamic Scheduling: The software dynamically adjusts schedules based on changing demands or unexpected delays in production, ensuring that resources are optimized and production targets are met.
2. Job Process, Machines, and Labor Allocation
a. Job Process Management: Each production job is clearly defined, specifying the necessary raw materials, semi-finished goods, machines, and labor. The system tracks each job from initiation to completion.
b. Machine Allocation: Machines that are registered and configured in the ERP system are allocated based on their availability, capacity, and efficiency.
c. Labor Assignment: Labor resources are also assigned to jobs based on skill sets, availability, and production requirements, ensuring the right people are handling the right tasks.
3. Work Order Planning
a. Batch Planning: Multiple work orders can be processed together in batch mode, grouping similar jobs or products to optimize machine usage and minimize setup times.
b. Capacity Planning: The system can also operate in capacity planning mode, allowing users to evaluate the available production capacity, forecast potential bottlenecks, and adjust schedules accordingly. This ensures that the workload is balanced and the production runs smoothly without overloading machines or labor.
4. Feasibility and Optimization
a. The ERP software provides users with real-time data on current production capacity, material availability, and labor scheduling, offering suggestions for the most feasible production schedule.
Optimized Workflow: By considering machine and labor constraints, the system helps optimize workflow, ensuring that production is done in the most time-efficient and resource-effective manner.
Key Benefits:
Improved Efficiency: By automating production planning and control, the system reduces manual errors, saves time, and ensures that production runs smoothly.
Flexibility: The ability to switch between batch and capacity planning modes provides flexibility in managing both short-term and long-term production schedules.
Maximized Resource Utilization: Optimized scheduling ensures that machines, labor, and materials are used effectively, minimizing waste and downtime.
Enhanced Decision-Making: Real-time data insights into production schedules allow for quick adjustments, ensuring production goals are met on time.
This automated and flexible production planning system ensures that Peacksoft ERP enhances manufacturing efficiency and production control.
Read more on Production Planning & Control
Quality
Quality Inspection & Control (QC) in Peacksoft ERP ensures that all finished goods meet the required quality standards before they are moved to the next phase or delivered to customers. This module allows users to manage, track, and record quality checks to ensure consistent product standards.
Key Features of QC:
1. Quality Inspection Recording:
a. After the production of finished goods, quality inspections are carried out, and the results are recorded in the system.
b. Users can log inspection data, such as measurements, test results, and compliance with quality criteria, ensuring that all products adhere to company standards.
2. Inspection Parameters:
a. The system allows the setup of inspection parameters such as dimensions, weight, material properties, or functional performance that need to be checked.
b. Each product or batch can have specific quality control metrics based on its nature and industry requirements.
3. Pass/Fail Criteria:
a. The inspection results are evaluated against pre-defined pass/fail criteria.
b. If a product meets the quality standards, it is approved for the next step, whether it’s packaging, storage, or delivery. If it fails, the system can flag it for rework or rejection.
4. Inspection Reports:
a. Detailed inspection reports can be generated for each batch or production run, highlighting which items passed, failed, or required further attention.
b. These reports can serve as documentation for audits, customer inquiries, or internal quality control reviews.
5. Continuous Quality Improvement:
a. With insights gained from inspection data, companies can identify trends or common quality issues and take proactive measures to improve future production runs.
b. Quality control data can be fed back into the production process to fine-tune manufacturing techniques and prevent recurring issues.
Benefits of Quality Inspection & Control:
a. Consistency in Product Quality: By recording and enforcing strict quality inspections, companies ensure that all finished goods meet required standards, leading to greater customer satisfaction.
b. Reduced Defects: Early identification of quality issues helps reduce the number of defective products reaching the market, minimizing returns and complaints.
c. Data-Driven Decisions: Inspection data provides valuable insights into production processes, helping companies make informed decisions to improve quality and efficiency.
d. Compliance: The system ensures that goods meet both internal quality standards and industry regulations, which is critical for regulatory compliance in certain industries (e.g., pharmaceuticals, food production).
e. Improved Traceability: The ability to track quality inspections at every stage of production ensures better traceability and accountability for each batch of goods produced.
This module is critical for manufacturers who want to maintain high quality, reduce waste, and ensure that only defect-free products reach customers.
Read more on Quality Inspection & Control
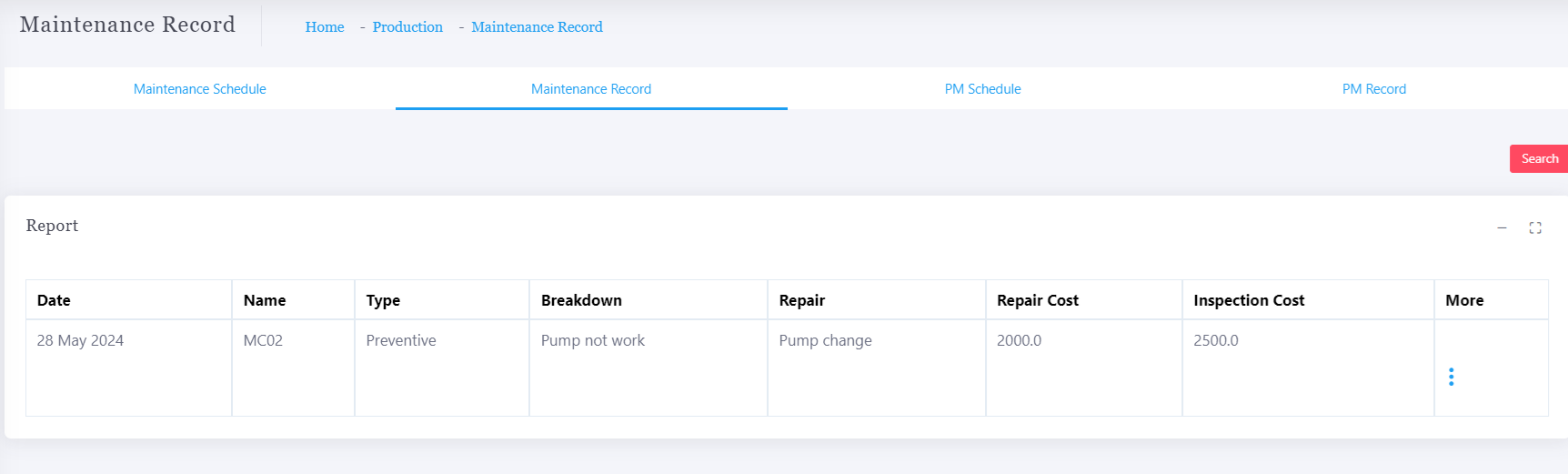
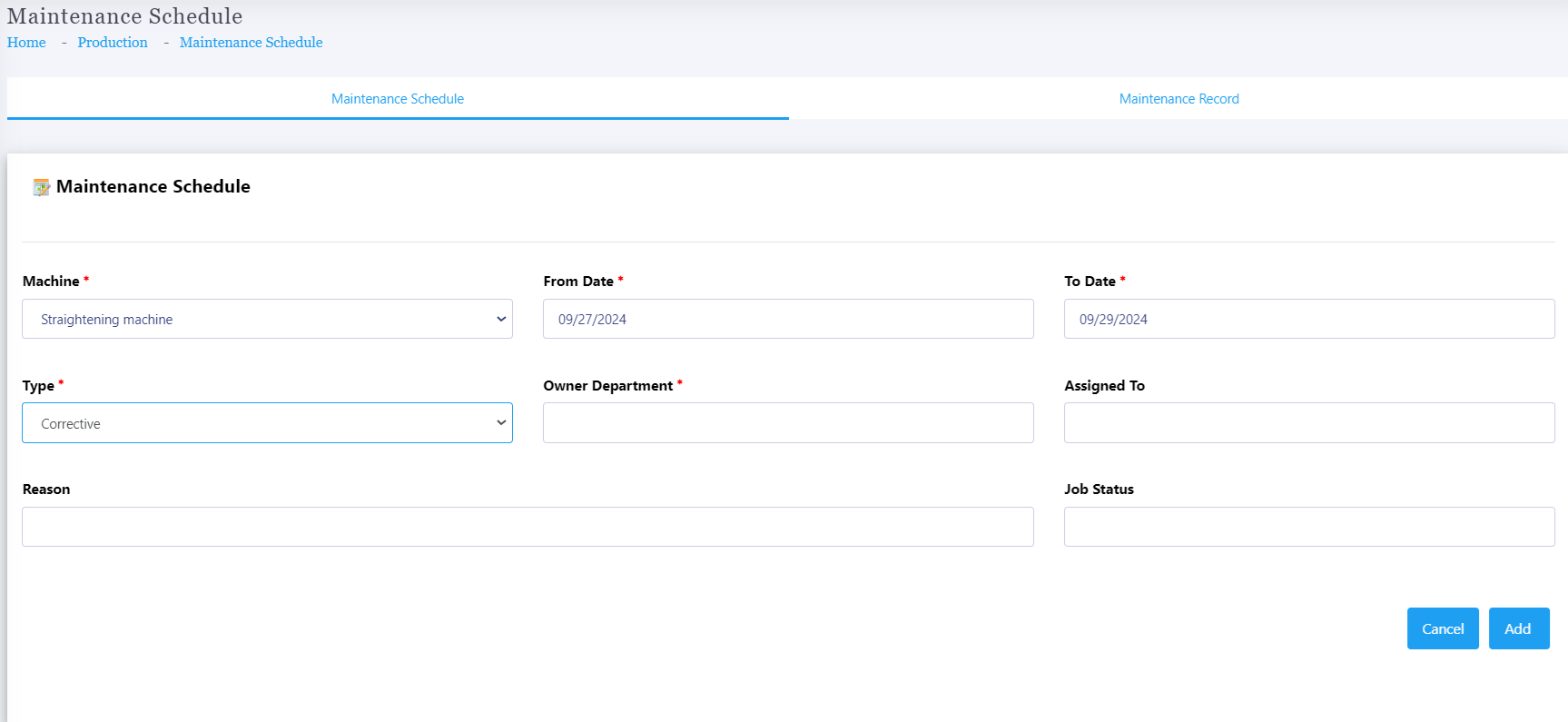
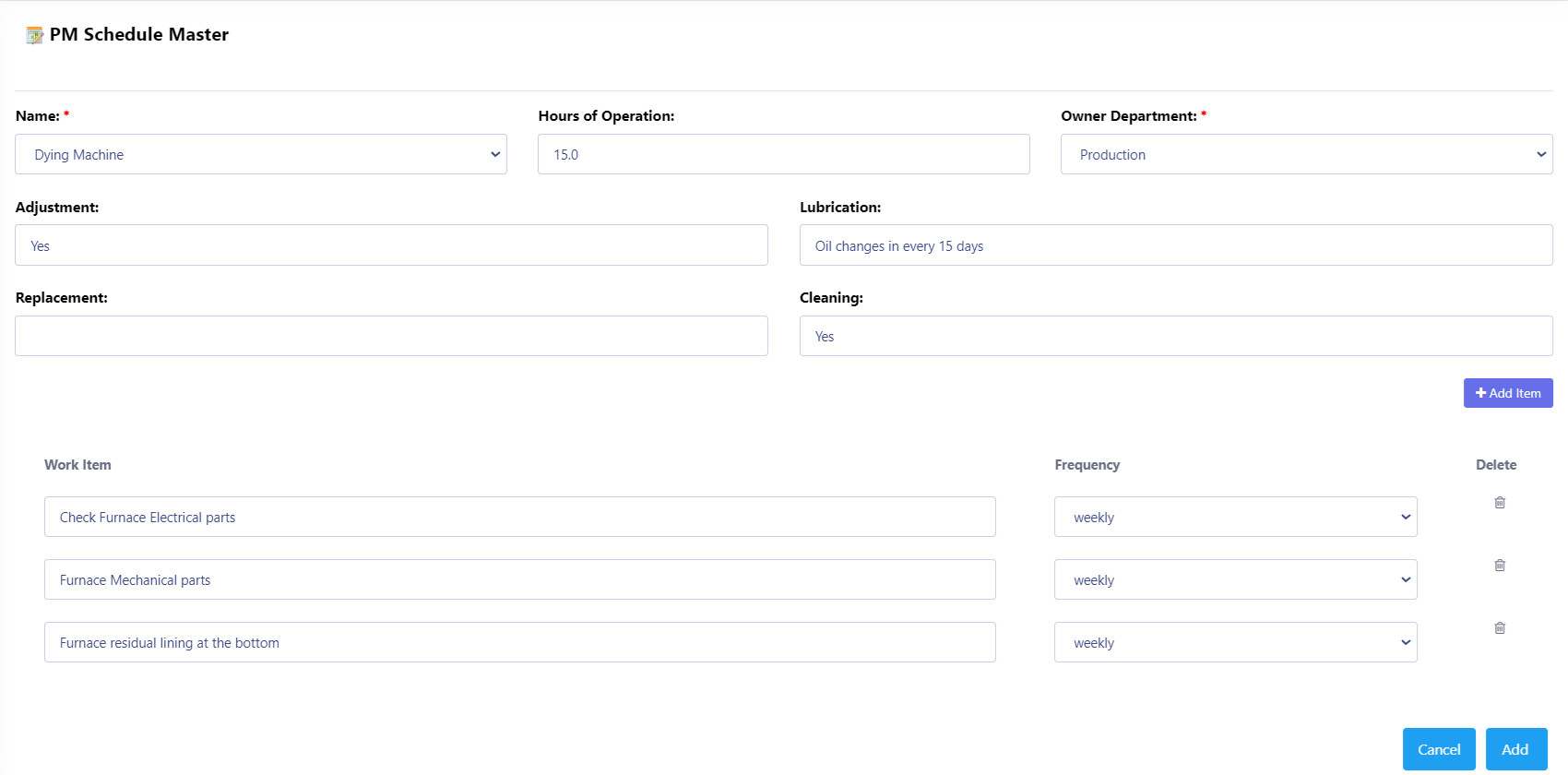
Production Machine Maintenance
Production Machine Maintenance refers to the regular inspection, servicing, and repair of machinery used in manufacturing to ensure they operate at optimal efficiency, minimize downtime, and extend their lifespan. Effective maintenance is crucial in any production environment, as equipment breakdowns can lead to costly delays, reduced productivity, and safety hazards.
Preventive Maintenance (PM):
Regular, scheduled maintenance activities aimed at preventing unexpected breakdowns.
Includes tasks like lubricating moving parts, tightening screws, replacing worn-out components, and inspecting the overall health of the machine.
Benefits:
Reduces the risk of sudden machine failure.
Extends the lifespan of machines.
Lowers the overall cost of repairs by addressing issues before they escalate.
Predictive Maintenance (PdM):
Uses data and sensors to predict when a machine might fail, allowing maintenance before an actual breakdown occurs.
Involves the use of technologies such as vibration analysis, thermography, and oil analysis to monitor machine health in real time.
Benefits:
Minimizes downtime as repairs can be scheduled before failure.
Reduces unnecessary maintenance tasks, as actions are taken based on data-driven insights.
Corrective Maintenance (CM):
Maintenance performed after a breakdown or failure has occurred.
Focused on repairing or replacing faulty components to get the machine back to working condition.
Benefits:
Directly addresses machine failures.
Necessary when breakdowns happen despite preventive measures.
Drawbacks:
Unplanned downtime can be costly.
Can lead to extended production delays.
Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM):
Similar to predictive maintenance but based on the actual condition of the equipment rather than time-based intervals.
Monitors specific parameters (e.g., temperature, vibration) to determine if maintenance is required.
Benefits:
Maintenance is performed only when needed, avoiding unnecessary tasks.
Increases machine availability and reduces unexpected failures.
Reactive Maintenance:
A run-to-failure approach where no maintenance is done until a machine breaks down.
This is a more costly strategy as it involves extended downtime and usually requires emergency repairs.
Benefits:
No need for scheduling or predictive systems.
Drawbacks:
Increases the likelihood of unscheduled downtime.
Expensive in terms of repairs and lost production.
Key Maintenance Activities
Inspection:
Regular visual and technical checks to identify early signs of wear and tear.
Check for leaks, unusual noises, vibration levels, and changes in operational performance.
Lubrication:
Ensuring that all moving parts are adequately lubricated to reduce friction and wear.
Periodically replacing oil and lubricants is vital for machine longevity.
Calibration:
Ensuring that machine settings and control parameters are within specified tolerances.
Regular calibration maintains production quality and machine precision.
Component Replacement:
Replacing worn or defective parts such as belts, bearings, and seals.
This avoids catastrophic failures that could damage the machine or lead to safety hazards.
Cleaning:
Cleaning machines to prevent contamination and ensure smooth operation.
Removing dust, debris, and other contaminants that could affect machine performance.
Alignment and Adjustment:
Ensuring the alignment of machine parts to prevent unnecessary stress on components.
Adjusting settings for proper operation and ensuring parts are operating under optimal conditions.
Common Tools for Machine Maintenance
Vibration Analyzers:
Used to detect misalignment, imbalance, or bearing issues by analyzing vibration patterns.
Thermal Imaging Cameras:
Used for detecting heat anomalies in machine components, indicating overheating or potential electrical issues.
Ultrasonic Detectors:
Help in detecting leaks, steam traps, and mechanical problems like improper lubrication.
Oil Analysis Kits:
Used to check oil quality, contamination, and wear metals, which indicate the condition of the machinery.
Laser Alignment Tools:
Precision tools to ensure proper alignment of machine components.
Maintenance Scheduling
Time-Based Maintenance:
Maintenance activities are scheduled based on predefined time intervals (daily, weekly, monthly, annually).
Suitable for machines with predictable wear and tear.
Usage-Based Maintenance:
Maintenance is scheduled based on machine operating hours or production cycles.
More efficient than time-based for machines that operate intermittently.
Event-Based Maintenance:
Maintenance triggered by specific events or conditions such as abnormal vibrations, temperature, or pressure changes.
Maintenance Management Tools
Benefits of Effective Machine Maintenance
Reduced Downtime:
Regular maintenance helps prevent unexpected breakdowns, leading to higher production uptime.
Extended Machine Lifespan:
Proper care and timely repairs extend the operational life of machinery, saving capital costs on replacements.
Improved Safety:
Well-maintained machines are less prone to failures that can lead to accidents or injuries.
Cost Savings:
Preventive and predictive maintenance reduce the need for costly emergency repairs and spare parts.
Minimizes losses due to production delays.
Enhanced Product Quality:
Machines that operate smoothly and consistently produce goods that meet quality standards, reducing defects and waste.
Conclusion
Production machine maintenance is critical to the smooth operation of any manufacturing or industrial process. Choosing the right maintenance strategy (preventive, predictive, etc.), scheduling regular inspections, using the correct tools, and leveraging technology like CMMS can significantly reduce downtime, improve efficiency, and maximize the lifespan of machinery.
Get Started with Peacksoft ERP Today
Intuitive solutions on cloud with integrated features like Accounting, Purchase, Sales, Production, CRM, Payroll, Inventory & Filing of all compliances. . Call us at +91-86608 58802 (M: 9845167247) to schedule a consultation.

 Manage sales through quotation by updating information and proceed to Sales order, Sales delivery , Sales invoice by click of few button.
Manage sales through quotation by updating information and proceed to Sales order, Sales delivery , Sales invoice by click of few button.
 Manage Purchases through order by updating information and proceed to GRN, Purchase Invoice by click of few buttons.
Manage Purchases through order by updating information and proceed to GRN, Purchase Invoice by click of few buttons.
 Comprehensive Inventory management features for small and mid size companies.
Comprehensive Inventory management features for small and mid size companies.
 Manufacturing
Manufacturing