Peacksoft ERP Quality Inspection & Control
Quality Inspection & Control in Production ERP systems like Peacksoft ERP plays a crucial role in maintaining product standards and ensuring that goods meet both customer and regulatory requirements. This module integrates with production workflows to ensure that quality checks occur at various stages of the manufacturing process. Here’s a detailed overview of how Quality Inspection & Control works in a Production ERP:1. Quality Inspection Process Overview:
Inspection Points: Inspections are scheduled at various stages of production, including:
a. Incoming Material Inspection: Raw materials and components are inspected when they arrive from suppliers.
b. In-Process Inspection: Quality checks are performed during various stages of manufacturing.
c. Final Product Inspection: The finished goods are inspected before they are packaged and shipped to customers.
Automated Triggers: The system automatically triggers quality inspections based on predefined criteria such as production steps, batch completion, or time intervals.
2. Inspection Criteria & Standards:
Predefined Quality Parameters: The system stores detailed inspection standards for each product, including tolerances, specifications, and acceptable quality levels (AQLs).
Customizable Checklists: Users can define inspection checklists that inspectors need to follow at each stage. These may include:
Visual inspections
Dimensional measurements
Functional tests
Material properties tests (e.g., hardness, composition)
Compliance Requirements: Inspections can be configured to ensure products meet regulatory compliance standards, including industry-specific certifications.
3. Integration with Bill of Materials (BOM) & Routing:
Linking Inspections with BOM: Inspections are tied to specific BOMs and production routes. Each material or component listed in the BOM can have associated quality inspection requirements.
Process-Linked Inspections: For in-process inspections, the ERP system links quality checks to specific job operations or production stages, ensuring that checks are done before moving on to the next step in the workflow.
4. Quality Control Data Collection:
Real-time Data Capture: During inspections, data is collected directly into the ERP system, either manually by inspectors or through automated tools like sensors and gauges integrated with the ERP.
Inspection Results: Inspectors log test results, and the system tracks pass/fail results for each item, including measured values against required specifications.
Non-conformance Reports (NCRs): If an item fails inspection, the system generates an NCR, detailing the reasons for failure and any corrective actions that need to be taken.
5. Defect Tracking & Root Cause Analysis:
Defect Identification: The system tracks the type of defects encountered during inspections, such as dimensional errors, material flaws, or functional failures.
Defect Categorization: Defects can be categorized by type, severity, or production step. This helps identify recurring problems and their sources.
Root Cause Analysis: The system provides tools for conducting root cause analysis (RCA) to determine why defects occurred and to implement corrective actions. It integrates with lean manufacturing or Six Sigma methodologies to minimize defects.
6. Rejection Handling & Rework:
Handling Rejected Items: For items that fail inspection, the system tracks what actions are taken, such as rework, scrap, or return to the supplier.
Rework Scheduling: The ERP can schedule rework tasks and allocate necessary resources (machines, labor) to correct defective products.
Waste Management: For items that cannot be reworked, the ERP tracks scrap and manages disposal procedures, updating inventory and costing automatically.
7. Supplier Quality Management:
Supplier Quality Tracking: Incoming material inspections can be linked to supplier performance, allowing companies to monitor and evaluate supplier quality over time.
Supplier Audits & Rating: Based on inspection results, the ERP can generate supplier scorecards, highlighting suppliers that consistently meet or fail quality standards.
8. Statistical Process Control (SPC) & Reporting:
SPC Tools: The ERP system includes SPC tools that allow users to monitor production processes in real time and ensure they stay within predefined control limits.
Trend Analysis & Reporting: The system generates detailed reports that analyze inspection results, defect rates, and other quality metrics over time. This helps identify trends and areas for improvement in the production process.
Real-time Dashboards: Quality metrics such as defect rates, inspection pass/fail rates, and rework quantities are displayed in real-time dashboards, providing immediate insight into production quality.
9. Compliance & Traceability:
Audit Trail: The system maintains a full audit trail of all inspections, providing documentation needed for audits or compliance reporting.
Batch/Lot Traceability: If a defect is found, the ERP system allows users to trace the defective item back through its production batch/lot and to its raw materials or supplier. This helps in identifying the source of quality issues.
Document Management: Quality-related documents such as inspection certificates, calibration records, and compliance certificates are stored in the ERP, ensuring all relevant information is easily accessible.
10. Alerts & Notifications:
Automated Alerts: The system automatically notifies relevant personnel (e.g., quality managers, production supervisors) if inspection results fall outside acceptable limits or if a batch fails.
Escalation Mechanism: If corrective actions are not taken promptly for quality issues, the system can escalate issues to higher management levels.
11. Key Benefits:
Reduced Defects & Rework: Early detection of quality issues reduces the need for expensive rework and minimizes the risk of delivering defective products to customers.
Improved Product Quality: Consistent inspections ensure that all products meet the company’s quality standards and customer expectations.
Enhanced Compliance: The system ensures that all products meet regulatory and compliance requirements, reducing the risk of fines or recalls.
Cost Savings: By catching defects early and minimizing rework, scrap, and warranty claims, the system helps reduce production costs.
Data-Driven Improvement: The system provides valuable data that can be used to refine production processes and improve overall quality.
Peacksoft ERP’s Quality Inspection & Control module provides a comprehensive solution for managing product quality throughout the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet the required standards and that defects are minimized through systematic inspections and data-driven insights.
Quality Inspection & Control
In Peacksoft ERP, Quality Check (QC) is integrated throughout the supply chain, from procurement to production and delivery. The QC module ensures that goods meet quality standards at every stage, helping businesses maintain consistency, compliance, and customer satisfaction.
Key Features of Quality Inspection in Peacksoft ERP:
1. QC Master Configuration:
a. Master Data Setup: The system requires users to configure QC master data for all goods involved in the production and supply chain. This includes defining specific quality parameters, sampling methods, and acceptable quality levels for each product or material.
b. Configurable QC Parameters: For each product or material, different QC attributes such as dimensional checks, material properties, functional tests, and visual inspections can be configured.
2. Instrumentation & Calibration:
a. Instrument Details: Users must input the details of the inspection instruments used, such as measuring devices, sensors, and testing equipment. Each instrument's specifications and calibration data are stored in the system.
b. Calibration Status Tracking: The system tracks the calibration status of instruments to ensure that only calibrated and certified devices are used in inspections. Calibration schedules can be configured, and alerts are generated when an instrument requires recalibration.
3. Sampling Plan & Procedures:
a. Sampling Methodology: Sampling is a critical aspect of quality control. The system allows users to define and manage sampling plans for each product, specifying sample size, sampling frequency, and inspection points.
b. Automated Sampling Plans: Based on the predefined QC master, Peacksoft ERP can suggest sampling procedures for different production batches or lots. This ensures that sampling is consistent and compliant with quality standards.
4. Stages of Quality Inspection:
a. Incoming Goods Inspection (Procurement Stage): Quality checks are performed when raw materials or components arrive from suppliers. Peacksoft ERP integrates with procurement to ensure that all incoming materials are inspected based on the QC master before they are accepted into inventory.
b. In-Process Inspection (Production Stage): Quality inspections are carried out during various stages of production to ensure that intermediate products meet the required specifications. This helps in identifying and correcting defects early in the production process.
c. Final Inspection (Pre-Delivery Stage): Before goods are shipped to customers, a final quality check is performed to ensure that finished goods meet all customer and regulatory standards.
5. Recording and Storing QC Data:
Real-Time Data Capture: During inspections, real-time data from the QC instruments is captured and recorded in the ERP system. Inspectors can also manually input results and notes.
Defect Logging: Any defects or non-conformities found during inspections are recorded. The system allows for detailed tracking of defect types, root causes, and corrective actions taken.
Inspection History: Each product or material has a complete QC history, including all inspections, defects found, and corrective actions. This history helps in audits and traceability.
Quality Master
QC Master
QC master has the details of inspection parameters with their reference values, measuring instrument and sampling plan configuration.
For setting generic test paramters, user needs to create Global test parameters.
Instrument Calibration
It captures last calibration details and next claibration due date. It also shows user alert for days remaining.
QC dashboard also shows quick status of calibration due alert for instrument.



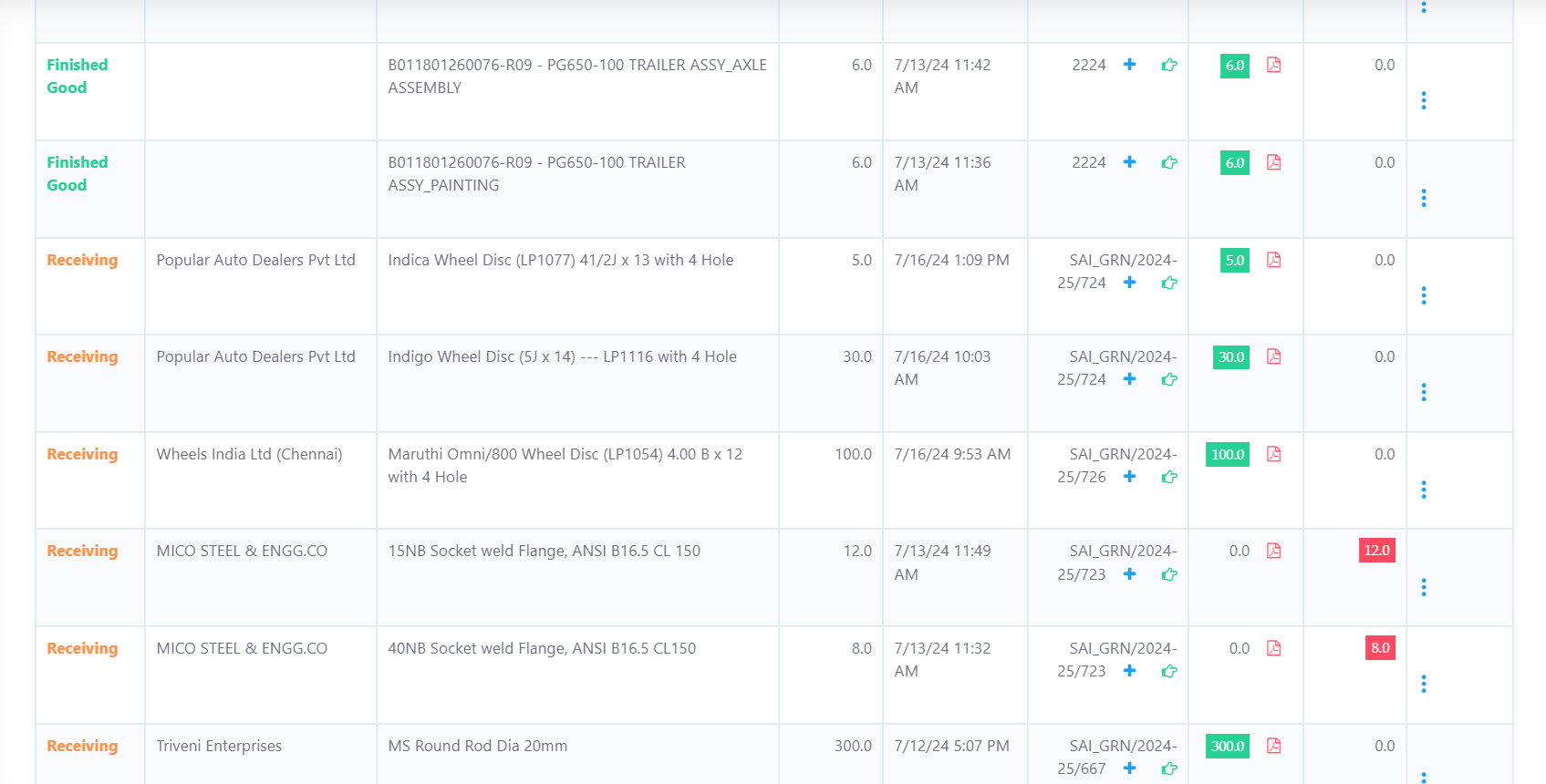
Sample Inspection
In Peacksoft ERP's Quality Inspection module, the process of quality control (QC) for raw materials (RM) after Goods Receipt Note (GRN) or finished goods after production completion follows a structured flow to ensure effective inspection and decision-making. The system offers both detailed sample-based inspections and shallow QC inspections, depending on the user's requirements.
Quality Inspection Workflow:
1. Initiation of QC Request:
A QC request is automatically raised or manually created after GRN for raw materials or after production completion for finished goods.
The request contains the essential details:
Item name and description
Quantity to be inspected
Environment and context for the inspection (e.g., storage conditions, temperature)
Sampling requirements, such as how many samples to test, which inspection methods to use, and acceptable quality limits.
2. Inspection Process:
The Quality Department is notified of the inspection request through the system. The QC team can now proceed with the inspection based on predefined QC parameters.
Sampling-based Inspection: For more detailed inspections, the system follows a sampling plan as defined in the QC master. The team captures detailed measurements and test results for each sample.
The inspection results for each sample are logged, including test values, observations, and defect details.
The results are aggregated, and the system provides insights on accepted and rejected quantities based on the predefined acceptable quality limits (AQL).
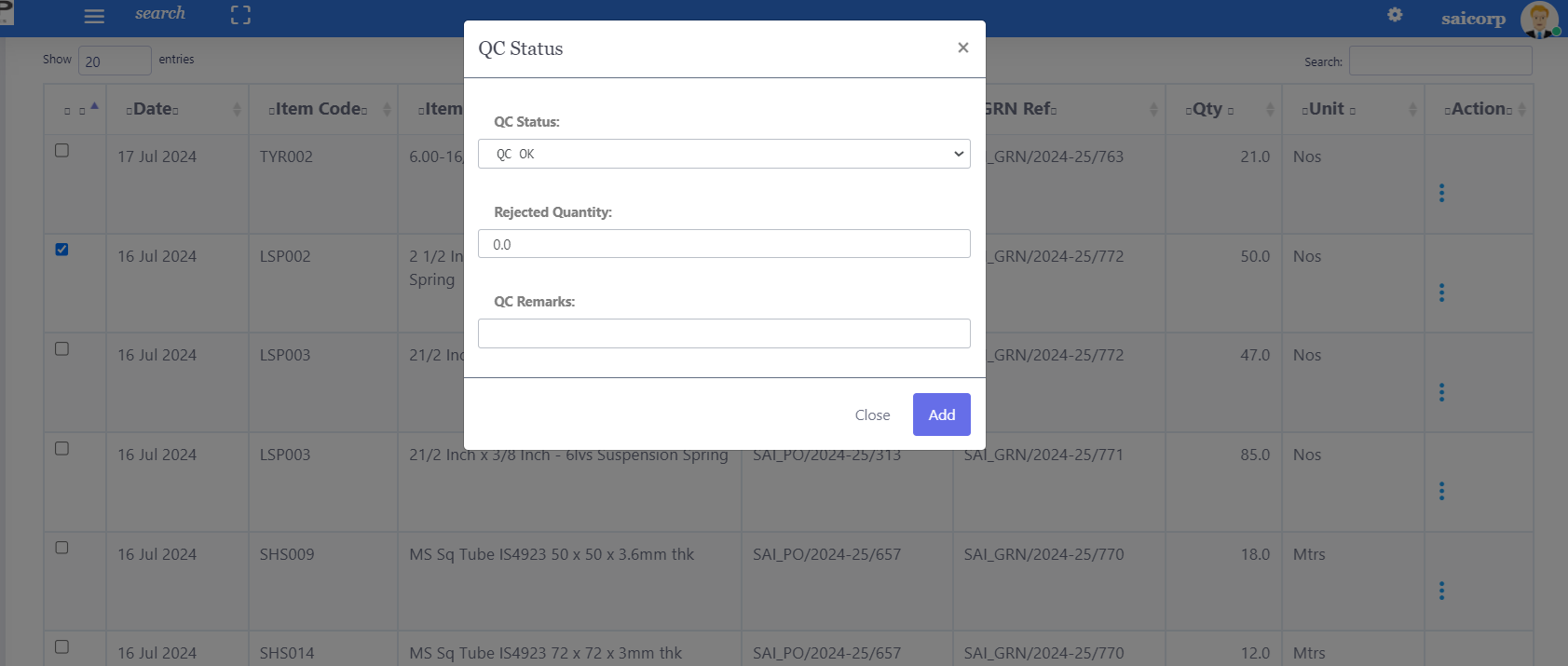
3. Shallow QC Inspection Option:
For cases where a detailed inspection isn’t necessary, Peacksoft ERP provides the option for a shallow QC inspection.
Instead of capturing detailed measurement results, the user can update:
QC Status: “QC OK” for accepted items or “Rejected” for failed inspections.
Rejected Quantity: If some items do not meet quality standards, the system records how many were rejected.
QC Comments: A brief summary or reason for rejection if applicable.
This simplified process allows for quick QC approvals or rejections, especially for low-risk or bulk goods.
4. QC Dashboard and Reports:
The QC Dashboard provides a real-time overview of ongoing and completed inspections, displaying key metrics such as:
Accepted quantity vs. Rejected quantity for each inspection.
Inspection status (e.g., in progress, completed, pending).
Detailed QC reports can be generated to analyze:
Inspection results per sample
Trends in rejections or defects
Compliance with quality standards over time
These reports help in tracking overall quality performance and identifying areas of improvement.
5. Outcome and Further Action:
Based on the inspection results, the next steps are automatically triggered in the system:
If the items are QC approved, they are moved into inventory or marked as ready for delivery.
If the items are rejected, they are quarantined, and further action, such as rework, return to supplier, or disposal, can be initiated.
Quality notes and detailed inspection results are stored in the system for future reference and audit purposes.
Quality inspection Results
In Peacksoft ERP's Quality Control (QC) module, the Inspection Result and Inspection Report are essential steps in determining the quality of goods, whether at the raw material stage, in production, or for finished goods.
Inspection Result:
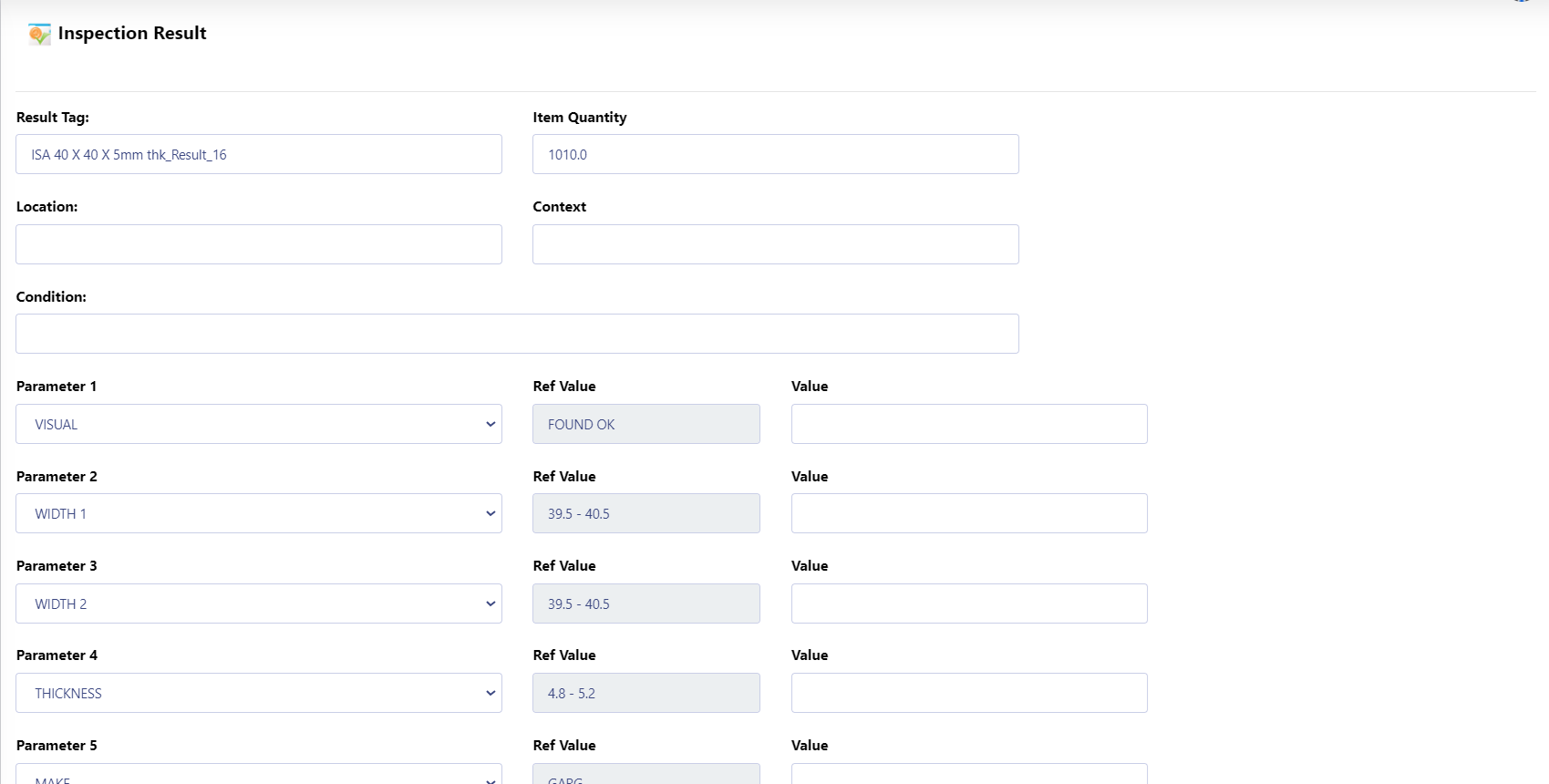
Sample Inspection:
During the inspection process, the system captures detailed test values for each sample against the parameters specified in the QC master.
For each sample tested, multiple parameters (e.g., dimensions, material strength, etc.) are evaluated and recorded.
The results for these parameters are input into the system for each sample, creating a detailed record of the inspection process.
Pass/Fail Status:
Based on the values entered and the acceptable ranges defined in the QC master, the system automatically calculates whether the sample passes or fails.
If all parameter values are within the defined limits, the sample will receive a "Passed" status.
If any parameter falls outside the acceptable range, the sample is marked as "Failed."
The results for each sample are stored, allowing the QC team to review them before making a final decision.
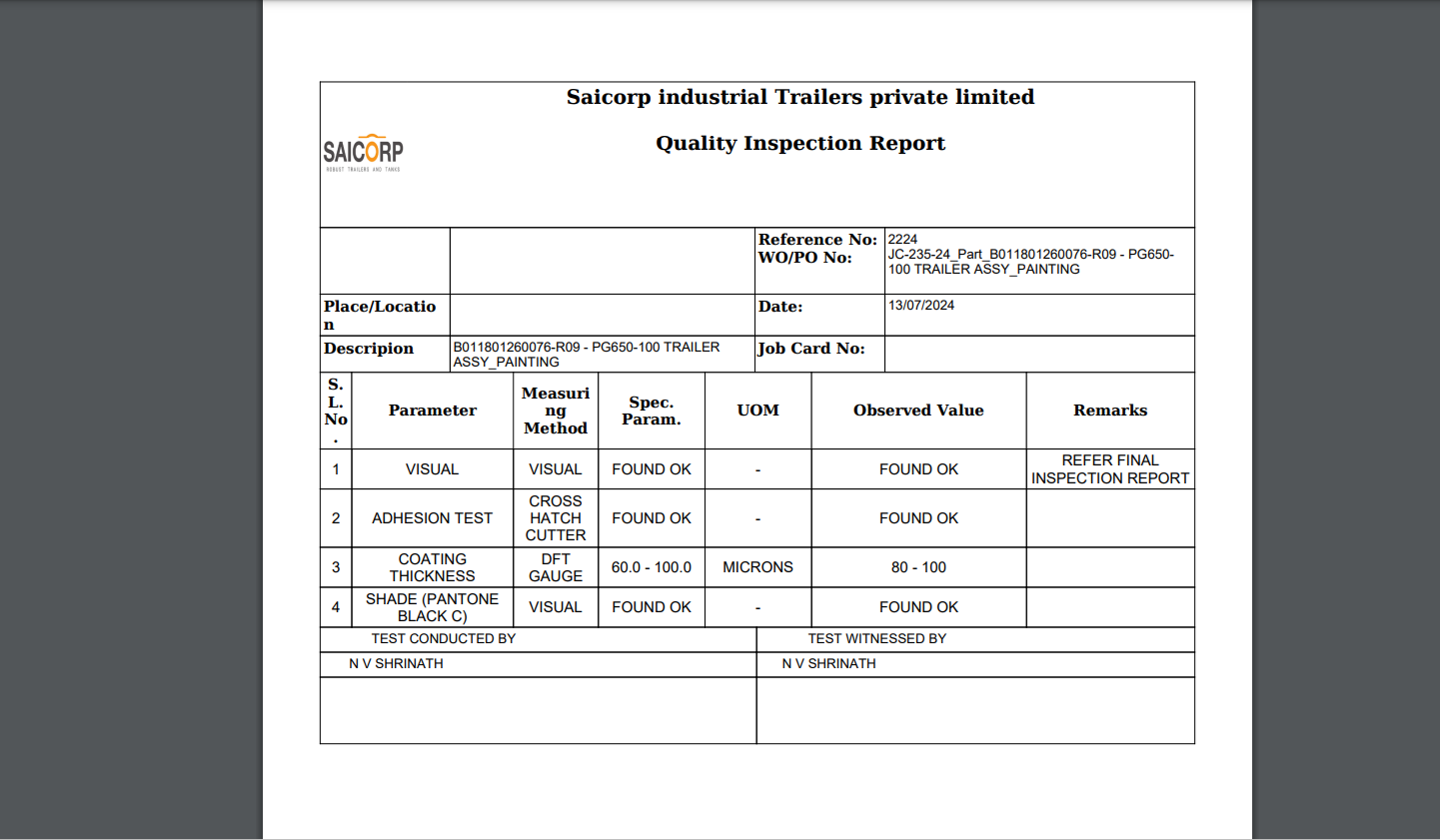
Inspection Report:
Consolidated Results:
Once all sample results are captured, the ERP generates a consolidated inspection result.
The consolidated view summarizes the performance of all samples tested, showing which samples passed and which failed.
For each parameter tested, the report highlights the actual values obtained and whether they meet the required quality criteria.
Acceptance or Rejection:
The user (QC manager or relevant personnel) reviews the consolidated results and makes the decision to accept or reject the inspection.
This discretion allows for flexibility in cases where minor deviations are present but may still be acceptable for use.
Alternatively, if a significant number of samples fail, the entire batch may be rejected, or specific steps may be taken to address the issues.
Final Inspection Report:
After reviewing the results and making the final decision, the system allows the user to generate an inspection report.
This report contains the detailed test values for each sample and parameter, as well as the overall pass/fail status of the inspection.
It also includes a summary section where the QC team can provide final comments, including any corrective actions required if the batch is rejected.
The report can be exported for auditing, compliance, or shared with other departments such as production or procurement.
The Inspection Result and Inspection Report ensure that quality checks are systematic and that decision-making is based on accurate data, enabling users to maintain high standards of quality control throughout the production process.


Get Started with Peacksoft ERP Today
Intuitive solutions on cloud with integrated features like Accounting, Purchase, Sales, Production, CRM, Payroll, Inventory & Filing of all compliances. . Call us at +91-86608 58802 (M: 9845167247) to schedule a consultation.

 Manage sales through quotation by updating information and proceed to Sales order, Sales delivery , Sales invoice by click of few button.
Manage sales through quotation by updating information and proceed to Sales order, Sales delivery , Sales invoice by click of few button.
 Manage Purchases through order by updating information and proceed to GRN, Purchase Invoice by click of few buttons.
Manage Purchases through order by updating information and proceed to GRN, Purchase Invoice by click of few buttons.
 Comprehensive Inventory management features for small and mid size companies.
Comprehensive Inventory management features for small and mid size companies.
 Manufacturing
Manufacturing